Dependency Scanning (ULTIMATE)
Introduced in GitLab Ultimate 10.7.
Overview
If you are using GitLab CI/CD, you can analyze your dependencies for known vulnerabilities using Dependency Scanning.
You can take advantage of Dependency Scanning by either including the CI job
in your existing .gitlab-ci.yml file or by implicitly using
Auto Dependency Scanning
that is provided by Auto DevOps.
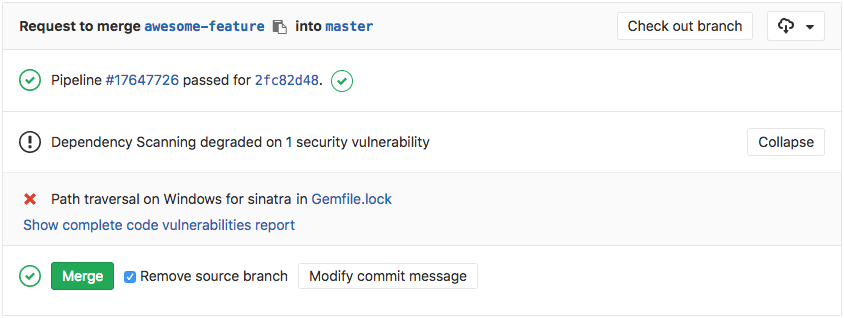
GitLab checks the Dependency Scanning report, compares the found vulnerabilities between the source and target branches, and shows the information right on the merge request.
The results are sorted by the severity of the vulnerability:
- Critical
- High
- Medium
- Low
- Unknown
- Everything else
Use cases
It helps to automatically find security vulnerabilities in your dependencies while you are developing and testing your applications. For example when your application is using an external (open source) library which is known to be vulnerable.
Requirements
To run a Dependency Scanning job, you need GitLab Runner with the
docker or
kubernetes
executor running in privileged mode. If you're using the shared Runners on GitLab.com,
this is enabled by default.
Supported languages and package managers
The following languages and dependency managers are supported.
| Language (package managers) | Supported | Scan tool(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Java (Gradle) | not currently (issue) | not available |
| Java (Maven) | yes | gemnasium |
| JavaScript (npm, yarn) | yes | gemnasium, Retire.js |
| Go (Golang) | not currently (issue) | not available |
| PHP (Composer) | yes | gemnasium |
Python (pip) (only requirements.txt supported) |
yes | gemnasium |
| Python (Pipfile) | not currently (issue) | not available |
| Python (poetry) | not currently (issue) | not available |
| Ruby (gem) | yes | gemnasium, bundler-audit |
Remote checks
While some tools pull a local database to check vulnerabilities, some others like Gemnasium require sending data to GitLab central servers to analyze them:
- Gemnasium scans the dependencies of your project locally and sends a list of packages to GitLab central servers.
- The servers return the list of known vulnerabilities for all versions of these packages.
- The client picks up the relevant vulnerabilities by comparing with the versions of the packages that are used by the project.
The Gemnasium client does NOT send the exact package versions your project relies on.
You can disable the remote checks by using
the DS_DISABLE_REMOTE_CHECKS environment variable and setting it to true.
Configuration
For GitLab 11.9 and later, to enable Dependency Scanning, you must
include the
Dependency-Scanning.gitlab-ci.yml template
that's provided as a part of your GitLab installation.
For GitLab versions earlier than 11.9, you can copy and use the job as defined
that template.
Add the following to your .gitlab-ci.yml file:
include:
template: Dependency-Scanning.gitlab-ci.ymlThe included template will create a dependency_scanning job in your CI/CD
pipeline and scan your project's source code for possible vulnerabilities.
The results will be saved as a Dependency Scanning report artifact that you can later download and analyze. Due to implementation limitations, we always take the latest Dependency Scanning artifact available.
Customizing the Dependency Scanning settings
The Dependency Scanning settings can be changed through environment variables by using the
variables parameter in .gitlab-ci.yml.
For example:
include:
template: Dependency-Scanning.gitlab-ci.yml
variables:
DS_DISABLE_REMOTE_CHECKS: trueBecause template is evaluated before the pipeline configuration, the last mention of the variable will take precedence.
Overriding the Dependency Scanning template
If you want to override the job definition (for example, change properties like
variables or dependencies), you need to declare a dependency_scanning job
after the template inclusion and specify any additional keys under it. For example:
include:
template: Dependency-Scanning.gitlab-ci.yml
dependency_scanning:
variables:
CI_DEBUG_TRACE: "true"Available variables
Dependency Scanning can be configured using environment variables.
| Environment variable | Function |
|---|---|
DS_ANALYZER_IMAGES |
Comma separated list of custom images. The official default images are still enabled. Read more about customizing analyzers. |
DS_ANALYZER_IMAGE_PREFIX |
Override the name of the Docker registry providing the official default images (proxy). Read more about customizing analyzers. |
DS_ANALYZER_IMAGE_TAG |
Override the Docker tag of the official default images. Read more about customizing analyzers. |
DS_PYTHON_VERSION |
Version of Python. If set to 2, dependencies are installed using Python 2.7 instead of Python 3.6. (Introduced in GitLab 12.1) |
DS_PIP_DEPENDENCY_PATH |
Path to load Python pip dependencies from. (Introduced in GitLab 12.2) |
DS_DEFAULT_ANALYZERS |
Override the names of the official default images. Read more about customizing analyzers. |
DS_DISABLE_REMOTE_CHECKS |
Do not send any data to GitLab. Used in the Gemnasium analyzer. |
DS_PULL_ANALYZER_IMAGES |
Pull the images from the Docker registry (set to 0 to disable). |
DS_EXCLUDED_PATHS |
Exclude vulnerabilities from output based on the paths. A comma-separated list of patterns. Patterns can be globs, file or folder paths. Parent directories will also match patterns. |
DS_DOCKER_CLIENT_NEGOTIATION_TIMEOUT |
Time limit for Docker client negotiation. Timeouts are parsed using Go's ParseDuration. Valid time units are ns, us (or µs), ms, s, m, h. For example, 300ms, 1.5h, or 2h45m. |
DS_PULL_ANALYZER_IMAGE_TIMEOUT |
Time limit when pulling the image of an analyzer. Timeouts are parsed using Go's ParseDuration. Valid time units are ns, us (or µs), ms, s, m, h. For example, 300ms, 1.5h, or 2h45m. |
DS_RUN_ANALYZER_TIMEOUT |
Time limit when running an analyzer. Timeouts are parsed using Go's ParseDuration. Valid time units are ns, us (or µs), ms, s, m, h. For example, 300ms, 1.5h, or 2h45m. |
PIP_INDEX_URL |
Base URL of Python Package Index (default https://pypi.org/simple). |
PIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URL |
Array of extra URLs of package indexes to use in addition to PIP_INDEX_URL. Comma separated. |
Reports JSON format
CAUTION: Caution: The JSON report artifacts are not a public API of Dependency Scanning and their format may change in future.
The Dependency Scanning tool emits a JSON report file. Here is an example of the report structure with all important parts of it highlighted:
{
"version": "2.0",
"vulnerabilities": [
{
"category": "dependency_scanning",
"name": "Regular Expression Denial of Service",
"message": "Regular Expression Denial of Service in debug",
"description": "The debug module is vulnerable to regular expression denial of service when untrusted user input is passed into the `o` formatter. It takes around 50k characters to block for 2 seconds making this a low severity issue.",
"cve": "yarn.lock:debug:gemnasium:37283ed4-0380-40d7-ada7-2d994afcc62a",
"severity": "Unknown",
"solution": "Upgrade to latest versions.",
"scanner": {
"id": "gemnasium",
"name": "Gemnasium"
},
"location": {
"file": "yarn.lock",
"dependency": {
"package": {
"name": "debug"
},
"version": "1.0.5"
}
},
"identifiers": [
{
"type": "gemnasium",
"name": "Gemnasium-37283ed4-0380-40d7-ada7-2d994afcc62a",
"value": "37283ed4-0380-40d7-ada7-2d994afcc62a",
"url": "https://deps.sec.gitlab.com/packages/npm/debug/versions/1.0.5/advisories"
}
],
"links": [
{
"url": "https://nodesecurity.io/advisories/534"
},
{
"url": "https://github.com/visionmedia/debug/issues/501"
},
{
"url": "https://github.com/visionmedia/debug/pull/504"
}
]
},
{
"category": "dependency_scanning",
"name": "Authentication bypass via incorrect DOM traversal and canonicalization",
"message": "Authentication bypass via incorrect DOM traversal and canonicalization in saml2-js",
"description": "Some XML DOM traversal and canonicalization APIs may be inconsistent in handling of comments within XML nodes. Incorrect use of these APIs by some SAML libraries results in incorrect parsing of the inner text of XML nodes such that any inner text after the comment is lost prior to cryptographically signing the SAML message. Text after the comment therefore has no impact on the signature on the SAML message.\r\n\r\nA remote attacker can modify SAML content for a SAML service provider without invalidating the cryptographic signature, which may allow attackers to bypass primary authentication for the affected SAML service provider.",
"cve": "yarn.lock:saml2-js:gemnasium:9952e574-7b5b-46fa-a270-aeb694198a98",
"severity": "Unknown",
"solution": "Upgrade to fixed version.\r\n",
"scanner": {
"id": "gemnasium",
"name": "Gemnasium"
},
"location": {
"file": "yarn.lock",
"dependency": {
"package": {
"name": "saml2-js"
},
"version": "1.5.0"
}
},
"identifiers": [
{
"type": "gemnasium",
"name": "Gemnasium-9952e574-7b5b-46fa-a270-aeb694198a98",
"value": "9952e574-7b5b-46fa-a270-aeb694198a98",
"url": "https://deps.sec.gitlab.com/packages/npm/saml2-js/versions/1.5.0/advisories"
},
{
"type": "cve",
"name": "CVE-2017-11429",
"value": "CVE-2017-11429",
"url": "https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-11429"
}
],
"links": [
{
"url": "https://github.com/Clever/saml2/commit/3546cb61fd541f219abda364c5b919633609ef3d#diff-af730f9f738de1c9ad87596df3f6de84R279"
},
{
"url": "https://github.com/Clever/saml2/issues/127"
},
{
"url": "https://www.kb.cert.org/vuls/id/475445"
}
]
}
],
"remediations": [
{
"fixes": [
{
"cve": "yarn.lock:saml2-js:gemnasium:9952e574-7b5b-46fa-a270-aeb694198a98"
}
],
"summary": "Upgrade saml2-js",
"diff": "ZGlmZiAtLWdpdCBhL...OR0d1ZUc2THh3UT09Cg==" // some content is omitted for brevity
}
]
}Here is the description of the report file structure nodes and their meaning. All fields are mandatory to be present in the report JSON unless stated otherwise. Presence of optional fields depends on the underlying analyzers being used.
| Report JSON node | Function |
|---|---|
version |
Report syntax version used to generate this JSON. |
vulnerabilities |
Array of vulnerability objects. |
vulnerabilities[].category |
Where this vulnerability belongs (SAST, Dependency Scanning etc.). For Dependency Scanning, it will always be dependency_scanning. |
vulnerabilities[].name |
Name of the vulnerability, this must not include the occurrence's specific information. Optional. |
vulnerabilities[].message |
A short text that describes the vulnerability, it may include occurrence's specific information. Optional. |
vulnerabilities[].description |
A long text that describes the vulnerability. Optional. |
vulnerabilities[].cve |
A fingerprint string value that represents a concrete occurrence of the vulnerability. It's used to determine whether two vulnerability occurrences are same or different. May not be 100% accurate. This is NOT a CVE. |
vulnerabilities[].severity |
How much the vulnerability impacts the software. Possible values: Undefined (an analyzer has not provided this info), Info, Unknown, Low, Medium, High, Critical. |
vulnerabilities[].confidence |
How reliable the vulnerability's assessment is. Possible values: Undefined (an analyzer has not provided this info), Ignore, Unknown, Experimental, Low, Medium, High, Confirmed. |
vulnerabilities[].solution |
Explanation of how to fix the vulnerability. Optional. |
vulnerabilities[].scanner |
A node that describes the analyzer used to find this vulnerability. |
vulnerabilities[].scanner.id |
Id of the scanner as a snake_case string. |
vulnerabilities[].scanner.name |
Name of the scanner, for display purposes. |
vulnerabilities[].location |
A node that tells where the vulnerability is located. |
vulnerabilities[].location.file |
Path to the dependencies file (e.g., yarn.lock). Optional. |
vulnerabilities[].location.dependency |
A node that describes the dependency of a project where the vulnerability is located. |
vulnerabilities[].location.dependency.package |
A node that provides the information on the package where the vulnerability is located. |
vulnerabilities[].location.dependency.package.name |
Name of the package where the vulnerability is located. Optional. |
vulnerabilities[].location.dependency.version |
Version of the vulnerable package. Optional. |
vulnerabilities[].identifiers |
An ordered array of references that identify a vulnerability on internal or external DBs. |
vulnerabilities[].identifiers[].type |
Type of the identifier. Possible values: common identifier types (among cve, cwe, osvdb, and usn) or analyzer-dependent ones (e.g. gemnasium for Gemnasium). |
vulnerabilities[].identifiers[].name |
Name of the identifier for display purpose. |
vulnerabilities[].identifiers[].value |
Value of the identifier for matching purpose. |
vulnerabilities[].identifiers[].url |
URL to identifier's documentation. Optional. |
vulnerabilities[].links |
An array of references to external documentation pieces or articles that describe the vulnerability further. Optional. |
vulnerabilities[].links[].name |
Name of the vulnerability details link. Optional. |
vulnerabilities[].links[].url |
URL of the vulnerability details document. Optional. |
remediations |
An array of objects containing information on cured vulnerabilities along with patch diffs to apply. Empty if no remediations provided by an underlying analyzer. |
remediations[].fixes |
An array of strings that represent references to vulnerabilities fixed by this particular remediation. |
remediations[].fixes[].cve |
A string value that describes a fixed vulnerability occurrence in the same format as vulnerabilities[].cve. |
remediations[].summary |
Overview of how the vulnerabilities have been fixed. |
remediations[].diff |
base64-encoded remediation code diff, compatible with git apply. |
Security Dashboard
The Security Dashboard is a good place to get an overview of all the security vulnerabilities in your groups and projects. Read more about the Security Dashboard.
Interacting with the vulnerabilities
Once a vulnerability is found, you can interact with it. Read more on how to interact with the vulnerabilities.
Vulnerabilities database update
For more information about the vulnerabilities database update, check the maintenance table.
Dependency List (ULTIMATE)
An additional benefit of Dependency Scanning is the ability to view your project's dependencies and their known vulnerabilities. Read more about the Dependency List.
Versioning and release process
Please check the Release Process documentation.
Contributing to the vulnerability database
You can search the gemnasium-db project to find a vulnerability in the Gemnasium database. You can also submit new vulnerabilities.